When a new lead comes in, time is ticking. The faster you connect them to the right salesperson, the better your chances of turning them into a customer.
That’s what lead routing does, it makes sure every lead goes to the right person at the right time. In 2025, using the right lead routing strategy isn’t optional; it’s the key to faster replies, fair workload, and higher sales.
What is lead routing software?
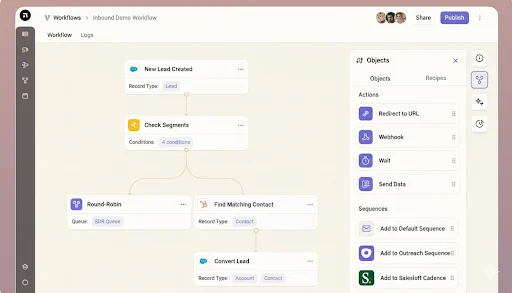
Lead routing software is a tool that automatically sends inquiries to new customers (known as ‘leads’) to the right salesperson to respond to them on time.
Example: Imagine a school office where many students ask different questions, related to books, sports, or exams. Instead of everyone shouting and getting confused, the office staff directs each student to the right teacher who can help.
That’s exactly what lead routing software does for a company.
A lead comes in → Software automatically figures out which salesperson will be the right match for the lead → and sends the lead to that person.
This way, no leads are lost, no salesperson is confused about “who should handle it,” and customers get their answers on time.
Manual vs Automated Lead Management
| Manual Lead Management (Old Way) | Automated Lead Management (Smart Way) |
|---|---|
| Slow replies – By the time you decide who should call, most customers have already bought from someone else. | Fast replies – Response time cut by 74%. Customers hear from you almost instantly. |
| Unfair workload – One person drowns in leads, while another has nothing to do. | Balanced work – Leads are shared fairly, so no one is overloaded. |
| Fights over leads – Team members argue about “who owns which lead.” | Clear rules – The System decides automatically who gets what. No arguments. |
| Leads vanish – Around 27% of leads just disappear. Nobody follows up. | Higher sales – Sales productivity jumps by 42%. No lead goes missing. |
| No accountability – People say, “I thought YOU were calling them.” | Better results – Conversions more than double (107% growth). Everyone knows their job. |
| Quality drops – Wrong person calls the wrong customer. | Right match – 91% of salespeople say lead quality improves. Customers talk to the right person. |
Lead Routing Techniques and When to Use Each
1. Rule-based Lead Routing
Rule-based routing is just a fancy term for “sending the right customer to the right salesperson.” Instead of giving leads randomly, you set up simple rules that decide who should handle which lead.
These rules can be based on many things, like where the customer is from, what product they are interested in, or which salesperson has the right skills. The idea is simple: match people with the person who understands their needs best.
Best for:
- Teams where people specialize in certain types of customers.
- Companies that divide areas by city or state.
- Businesses where industry knowledge matters.
Example:
We worked with a software company that set a simple rule:
- If a lead comes from a big company with 1000+ employees, it goes straight to their enterprise team.
- If the lead is from a small company, it goes to their inside sales team.
2. Round-Robin Lead Routing
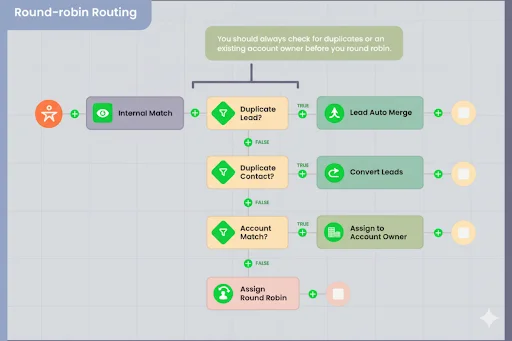
Round-robin routing is just a smart way of sharing new customers fairly among your sales team. Instead of giving all the work to one person, it passes leads around in a cycle, so everyone gets an equal chance.
Think of it like serving food at a table. First plate goes to Person A, second plate to Person B, third plate to Person C… and then back again to Person A. The same happens with leads.
Best for:
- Teams where everyone has almost the same skills.
- Businesses that get lots of leads and need a quick, fair way to distribute them.
- Companies that don’t want to overthink the process.
Extra twist –Weighted Round-Robin:
Sometimes, you may give more leads to your experienced salesperson and fewer to the new one. For example:
- Rockstar salesperson → 40% of leads
- Newbie salesperson → 20% of leads
3. Availability-Based Routing
Availability-based routing means sending a new customer to whoever in the team is free at that moment. Instead of waiting for the “perfect” person, the lead is quickly given to the next available rep, so the customer doesn’t have to wait.
Best for:
- Teams that respond instantly (like inside sales).
- Live chat or website inquiries.
- Teams are spread across different time zones. (E.g., London handles mornings, New York handles evenings).
Success Tips:
- Make sure your calendar is connected properly, so the system knows who is free.
- Team members must update their status honestly (“Available” or “Busy”).
- Always have a Plan B if everyone is stuck in a meeting.
4. Hierarchy-Based Routing
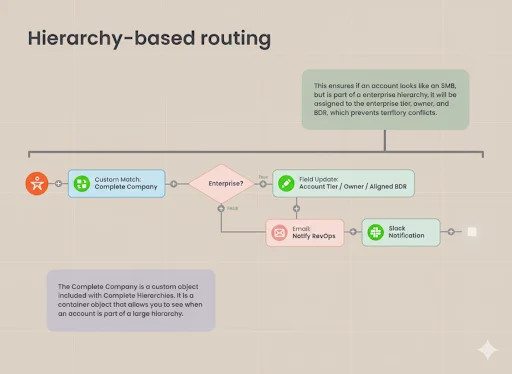
Hierarchy-based lead routing is about connecting a new lead to the right “parent” company account when that company has many branches or smaller divisions.
Think of it like a big family tree where one parent has many children. The system makes sure the lead doesn’t get lost and is linked to the correct main account.
Why it’s useful:
- Sales teams can see the full picture of a big company instead of working with bits and pieces.
- Leads from smaller branches are not lost or treated separately.
- It avoids confusion when handling global or multi-branch organizations.
5. Product-Based Lead Routing
Product-based lead routing simply means sending a new customer to the salesperson who knows that specific product best.
Instead of giving all leads to one general rep, you make sure the customer talks to the right expert from the start.
Example:
Think about Amazon. It’s one big company, but it offers many services like AWS (cloud), Prime (shopping + video), and Ads (advertising).
Building Your Lead Routing Strategy
Phase 1: Understand What’s Happening Now (Week 1-2)
Step 1: Check Your Current System
- Write down every step of how leads are handled right now.
- Look for problem areas where things get stuck or slowed.
- Measure how fast your team replies to new leads (you may be shocked!).
- Note how many leads actually turn into paying customers.
Step 2: Decide the Goal
- How fast do you want to reply to new leads? (Example: within 5 minutes or less).
- Set a clear target for how many leads should convert into sales.
- Make rules for fair workload so no one is overloaded.
- Plan how to treat important “must-win” customers.
Step 3: Draw the Ideal Flow
- Use a paper or whiteboard.
- Show where your leads come from and where they should go.
- Make a backup plan for when things don’t go as planned.
Phase 2: Create the System (Week 3-4)
Step 4: Make Rules for Sending Leads
Here’s a simple order most companies use:
- Send leads based on their location (territory).
- Send leads to the right rep if it’s an existing customer.
- Use lead scores (how interested they are).
- Send leads based on what product/service they want.
- Share new leads equally among the team using a round-robin.
- If none of the above fits, send them to a general queue for manual check.
Step 5: Set Up Lead Scoring
Keep it simple in the beginning. For example:
- High score if the person is a decision-maker (like a company director).
- High score if the company is big.
- High score if they check important pages (like “pricing”).
- Low score or negative marks for leads that are not useful (students, competitors, etc.).
Step 6: Connect Your Tools & Systems
- Connect one system at a time (CRM, email, etc.).
- Test carefully—send test leads first.
- Write down everything you do (helps avoid future confusion).
Phase 3: Test and Improve (Week 5-6)
Step 7: Pilot Testing Protocol
- Start with only 10% of your leads in the new system.
- Keep the old method running for safety.
- Track numbers closely.
- Ask your sales team for feedback daily. They’ll tell you if something’s not working.
Step 8: Improve Based on Real Data
- Change rules if needed.
- Adjust scoring points.
- Speed up any slow steps.
- Balance work between the team if one area is overloaded.
Phase 4: Roll Out Fully (Week 7 onward)
Step 9: Roll Out Slowly
- Don’t push 100% leads into the new system right away.
- Move step by step: 25%, then 50%, then 75%, and finally all leads.
- Give the team time to adjust—the change won’t feel too heavy this way.
Step 10: Keep Improving Always
- Check performance every week.
- Review rules monthly.
- Discuss bigger updates every 3 months.
- Once a year, ask: “Is this system still the best for us?”
Conclusion
At the end of the day, lead routing is all about delivering the correct customer to the correct individual at the right time.
When you do this well, no lead is wasted, your team works smoothly, and customers get answers faster.
In 2025, smart routing strategies will enable businesses to win more deals more quickly, and those that do not pursue it will continue accruing losses.
